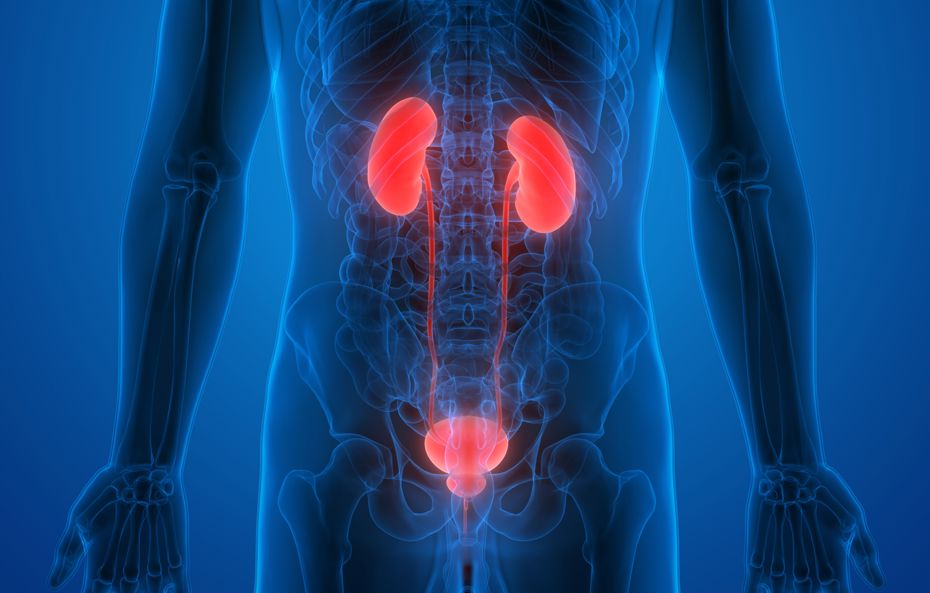
The Urinary System is responsible for the eliminating of waste and extra fluid in the body, by making and excreting urine.
It’s important that all parts of the urinary system work in partnership for normal urination to occur. The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The male urethra is in the shape of an s. The length of the urethra is approximately 20-27 cm. The prostate is located just below the bladder, the urethra passes through the prostate. The prostate produces the secretions in which the sperm swim and it contains also a prostate-specific antigen, PSA. Men have 2 muscular sphincters (valves), the internal sphincter (smooth muscle), which prevents semen from entering the bladder, and the external sphincter (striated muscle) which can be controlled voluntarily to prevent voiding.
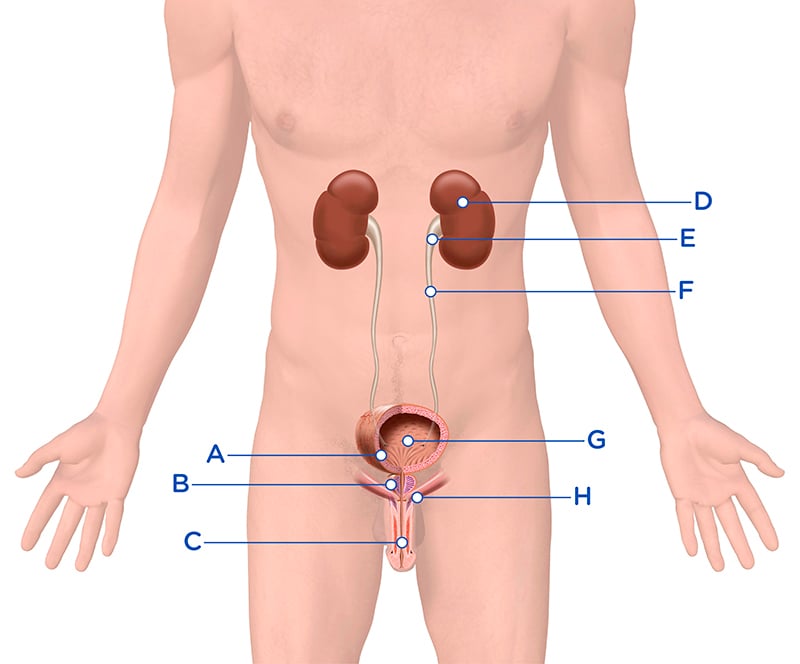
A = Internal sphincter
B = Prostate
C = Urethra
D = Kidneys
E = Renal Pelvis
F = Ureter
G = Bladder
H = External sphincter
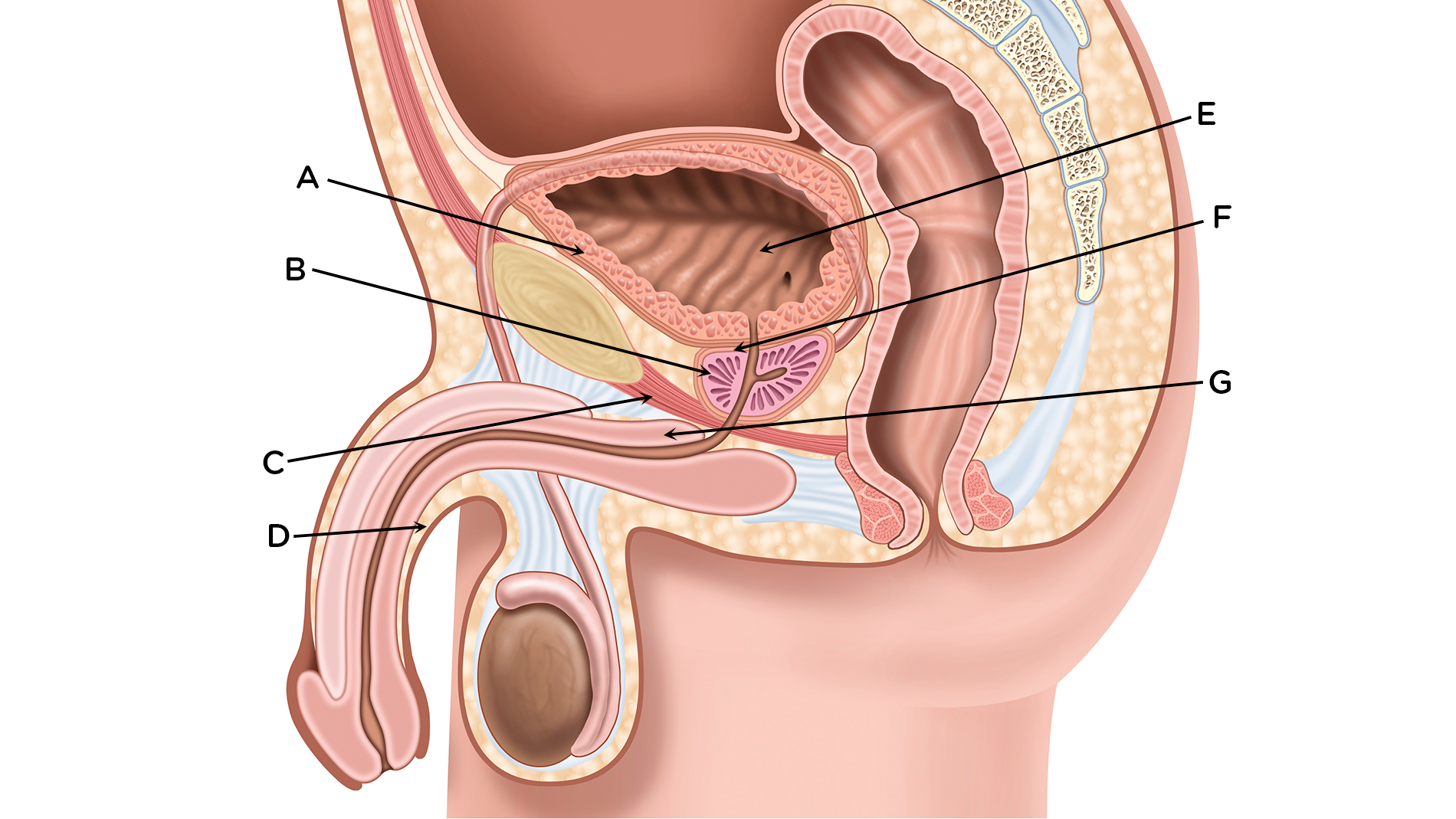
A = Detrusor muscle
B = Prostate gland
C = Pelvic floor
D = Urethra
E = Bladder
F = Internal sphincter
G = External sphincter