What is Urinary Incontinence?
With urinary incontinence, you experience involuntary leakage of urine due to loss of bladder control. While it's perfectly normal to feel embarrassed by this situation, you are not alone.
People often avoid seeking help since they find it embarrassing - which means the condition is sometimes left untreated. This is very unfortunate since the underlying cause is often treatable, and treatment can improve quality of life dramatically.
Urinary Incontinence Symptoms
The symptoms and severity of urinary incontinence range from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having the urge to urinate that’s so sudden and strong that you don’t get to the toilet in time. There are different types of incontinence and their symptoms can differ.

Types of Urinary Incontinence
The most common are stress, urge and overflow incontinence:
Stress Incontinence
This is loss of urine when you exert pressure - stress - on your bladder by coughing, sneezing, laughing, exercising, or lifting something heavy. Stress incontinence occurs when the sphincter muscle and/or the pelvic floor of the bladder is weakened. In women, this could be due to physical changes resulting from pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause. In men, removal of the prostate gland can lead to this type of incontinence. Treatment depends on the severity of your symptoms and ranges from behavior advice and physical therapy to pharmaceuticals and surgery.
Urge Incontinence
This is a sudden, intense urge to urinate, followed by an involuntary loss of urine. Your bladder muscle contracts and may give you a warning of only a few seconds to a minute to reach a toilet. With urge incontinence, you may need to urinate often, including throughout the night. Urge incontinence may be caused by urinary tract infections, bladder irritants (pharmaceuticals, foodstuff, etc.), urinary retention, bowel problems, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, injury, or nervous system damage associated with multiple sclerosis. If there's no known cause, urge incontinence is also called overactive bladder. Treatment depends on the severity of your symptoms and ranges from behavior advice and physical therapy to pharmaceuticals, catheterization, and surgery. Usually a combination of treatments is most effective.

Overflow Incontinence
If you frequently or constantly dribble urine, you may have overflow incontinence, which is an inability to empty your bladder. Sometimes you may feel as if you never completely empty your bladder. When you try to urinate, you may produce only a weak stream of urine. This type of incontinence may occur in people with a damaged bladder, blocked urethra, or nerve damage from diabetes and in men with prostate gland problems. Treatment depends on the severity of your symptoms and ranges from catheterization, behavior advice, and physical therapy to pharmaceuticals and surgery. Often times a combination of treatments is most effective.
Mixed Incontinence
If you experience symptoms of more than one type of urinary incontinence, such as stress incontinence and urge incontinence, you have mixed incontinence.
Other, less common types of incontinence include:
- Functional incontinence: Older adults or disabled people may experience incontinence simply because a physical or mental impairment keeps them from making it to the toilet in time. For example, a person with severe arthritis may not be able to unbutton his or her pants quickly enough.
- Total incontinence: This term is sometimes used to describe the continuous leaking of urine, day and night, or the periodic uncontrollable leaking of large volumes of urine. In such cases, the bladder has no storage capacity. Some people have this type of incontinence because they were born with an anatomical defect. It can be caused by injuries to the spinal cord or urinary system, or by an abnormal opening (fistula) between the bladder and an adjacent structure, such as the vagina. Treatment depends on the severity of your symptoms and ranges from catheterization, behavior advice, and physical therapy to pharmaceuticals and surgery, often in combination.

Causes of Urinary Incontinence
There are many possible causes of urinary incontinence:
- Your diet (both food and drink) and the use of certain medications can stimulate your bladder
- Other treatable medical conditions can also cause incontinence, including Urinary tract infections and Constipation
- Pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause all pose potential causes of urinary incontinence in women
- Men may experience bladder leakage as a result of an enlarged prostate
- Injuries or diseases affecting the nervous system can affect signals to the bladder, leading to the leaking of urine, these include Spinal Cord Injuries, Multiple Sclerosis, Spina Bifida, and Parkinson's Disease.
- Finally, urinary incontinence becomes more likely with age
Urinary Incontinence Treatment
If you are experiencing urinary leakage regularly, don't worry because there are lots of options out there for managing your bladder.
Depending on the severity of your urinary incontinence, your healthcare provider might suggest one of the following options:
- Lifestyle changes - usually around diet and exercise
- Behavioral interventions - such as pelvic floor exercises or bladder retraining
- Catheterization - allowing you to choose when and where you empty your bladder
- Surgery - although this is rare because, with catheterization, most people are able to completely manage their incontinence
LoFric Elle - Female
key:global.content-type: Product
The angle changes everything. This is the new way for women to self-catheterize. LoFric Elle is an innovative solution, easy to learn, use and teach.
Try product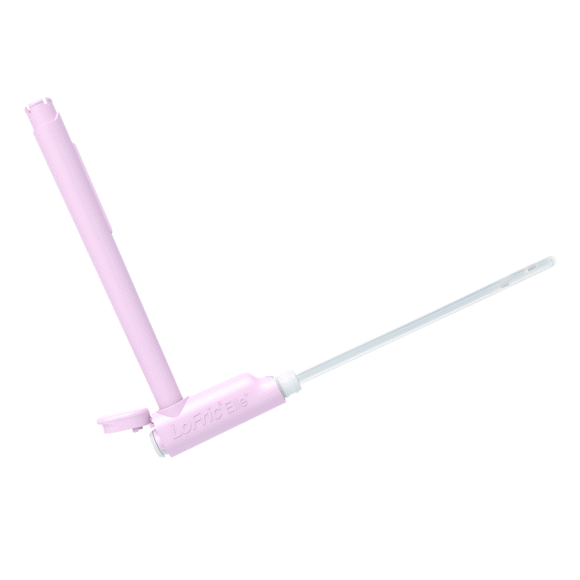
LoFric Origo - Male
key:global.content-type: Product
User-friendly and safe in a smart package. Specially developed for men, LoFric Origo is foldable to pocket size and easy to carry and use everywhere.
Try product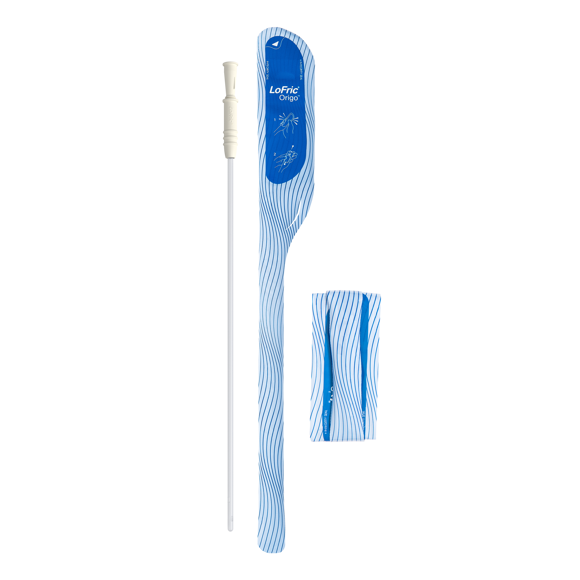
LoFric Hydro-Kit
key:global.content-type: Product
The all-in-one solution. LoFric Hydro-Kit has an integrated collection bag and is easy to use for men, women and children on the move.
Try product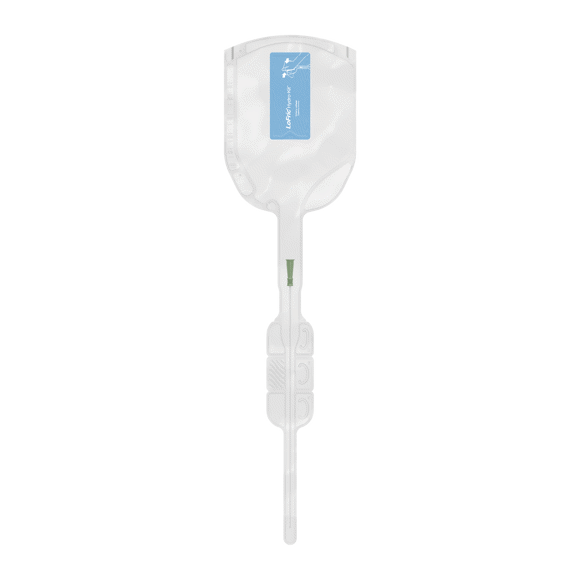
-
Treatment Options for Bladder Problems
In this section, we explore the treatment options available for bladder problems, one of which is catheters. Learn about the different types of catheters and how they are used.

-
Living with Bladder Problems
To live with a condition that requires you to catheterize on a regular basis may feel overwhelming in the beginning. Find comfort in the fact that you are not alone.

-
Bladder Products
LoFric is a complete solution for short- and long-term bladder management. Based on the unique Urotonic Surface Technology, LoFric enables intermittent catheterization in a safe and user-friendly way.