Improve women’s health – improve the world!
This bold claim may sound a little bombastic, but this is a message from the World Health Organization (WHO). Women’s health not only concerns women, but their families, communities, and societies at large. In other words – it’s a concern of high priority.
Generally, women face greater difficulties in getting the healthcare they need and it’s clear that changes are needed. The WHO calls for reforms to ensure that women are centrally involved in their care. We agree and want to contribute!
Our vision: To make it possible for all women to succeed with Intermittent Catheterization. This video explains how.
Female Bladder Problems
Women are more prone than men to get UTIs due to a number of reasons, e.g. the shorter urethra, hormonal changes, etc.
UTI in the figures
- About half of all women will experience UTI during their lifetime
- The risk of getting UTI is 3-4 times greater if you are a woman
- About 1/3 of all women by the age of 24 have had UTI
- Women between 16-35 years are about 35 times more likely to be affected by UTI than men
These figures might sound a little unfair but they have to do with how our bodies are built. Men’s longer urethras facilitate a natural bacteria washout every time they void. Also, the position of the female urethra, close to the rectum and vagina, is unfortunately beneficial for bacteria exchange.
UTIs are fairly common for sexually active women, although peeing before and after sex can help prevent infection. Women with diabetes are more likely to get a UTI because of the condition's impact on the immune system.
Other reasons are the use of birth control and antibiotics, which may disrupt normal vaginal flora. Also, genetic factors and estrogen levels are shown to have an impact.
Usage of urethral catheters increases the risk of UTI, and that’s why it is important to make a conscious catheter choice and use the correct technique. Hydrophilic-coated catheters are for example proven to reduce the risk of UTIs and are often preferred by users.
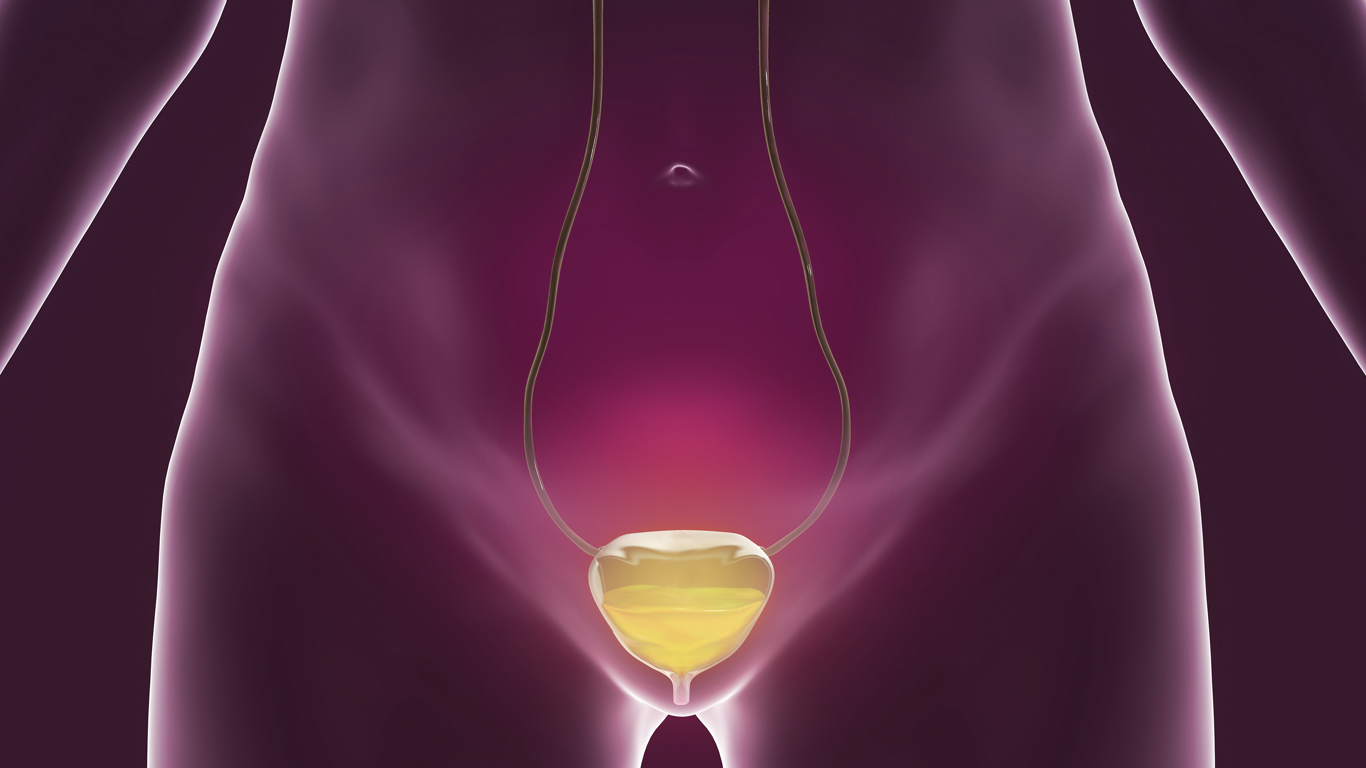

Another common problem in women is Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS). The term covers both genders but the overall prevalence is higher in women. LUTS includes symptoms like frequency, urgency, poor stream, and dribbling.
- Urinary incontinence is about 2,5 to 3 times more common in women.
- The risk of UTIs is 3-4 times greater in women.
- Overactive bladder is more common in women.
LUTS is divided into two main categories: Problems related to storage (if you're leaking urine) or voiding (if you can't empty your bladder).
If You're Leaking Urine
You may find that you accidentally leak a little wee when you cough, sneeze or exercise. This is referred to as stress incontinence and is common after pregnancy and childbirth.
Urine leakage is also common due to neurological diseases like MS, and/or because of an overactive bladder (OAB). The bladder contracts when it shouldn’t, causing leakage. This is referred to as urge incontinence.
Incontinence and storage problems are generally more common in women than in men.
If You Can't Empty Your Bladder
Urinary retention is the opposite of incontinence – you have trouble emptying your bladder completely. When there is urine left in the bladder, the risk of infections increases. If this is not resolved, the kidneys can be harmed.
Retention is quite unusual in women unless you have a neurological disease, prolapse or postoperative surgical complications. It’s common in elderly men where the retention can either be due to a mechanical barrier, such as an enlarged prostate, or impaired muscles of the bladder wall making them too weak to contract.
Intermittent Catheterization as the Solution

Many women struggle for years to find a solution to their bladder problems. One method that is sometimes overlooked, or even avoided, is intermittent catheterization (IC). IC may be a good solution to many of these problems, but women sometimes feel a bit resistant to IC. With that said – when you have overcome the barriers, it’s likely that you have found the solution to your bladder problems.
Does any of this sound familiar?
Anatomy and Positioning
To be frank, for a woman it’s not that easy to see where to enter the catheter, and you probably need a little bit more support when you first start. Body shape and sitting balance may often require the assistance of a caregiver, which can be embarrassing and uncomfortable.
Inaccessible Bathrooms
For many women, just the thought of going out without knowing if you will find an accessible bathroom is enough to stay home. Some women even drink less, to limit their visits to the toilet (don’t do that). Public toilets aren't always the most hygienic of places, and there may be anxiety over how to discreetly dispose of the catheter.
Yet Another Chore to Fit in
For some it seems messy and time-consuming and yet another thing to consider in the “life puzzle”, hindering social life and relationships, which are essential to emotional well-being. Many women doubt whether catheterization is compatible with a busy lifestyle, socializing, and work.
Fear of Concept
Many women experience shame, loss of dignity, and low self-esteem when they can’t urinate the normal way. Some think IC seems invasive and painful, it takes their femininity away and is associated with the elderly.
These fears are perfectly normal, but not always addressed by your healthcare professionals. If you recognize yourself in the above, please take the opportunity to discuss it with your clinician.
Choose your catheter carefully
- Give it an honest chance - your dedication will ensure the outcome!
- Evaluate different options - it’s very important to find a catheter that offers ergonomic control, is hygienic, and provides discreet storage and disposal
- Select a catheter that fits and supports your lifestyle and needs - not the other way round
- And finally - a good start is crucial in succeeding with intermittent catheterization. Demand attentive support from your healthcare provider and expect the most from your catheter.
The video below gives advice on how to self-catheterise.
How to Choose the Right Catheter
When you're new to catheterization, it makes sense to know what makes one catheter more right for you than another. Here we explore how to choose the right catheter for you.

Intermittent Catheterization (IC)
Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is the next best way to urinate, the way that mostly mimics the natural way of urinating. In this section you can watch animations to understand the whole procedure of IC, download catheterization instructions and more.

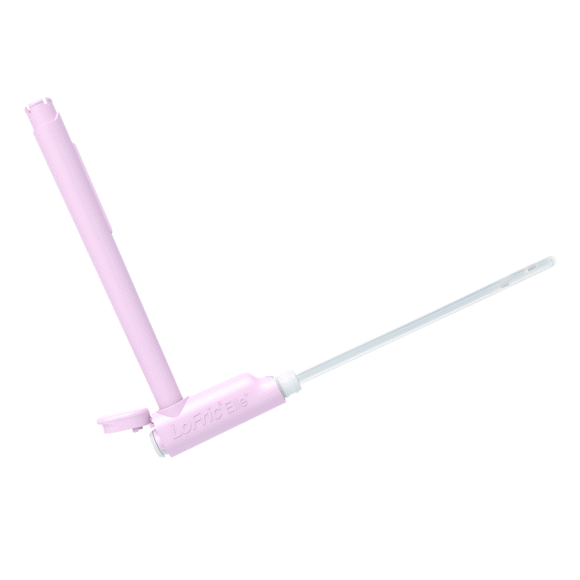
LoFric Elle - Female
key:global.content-type: Product
The angle changes everything. This is the new way for women to self-catheterize. LoFric Elle is an innovative solution, easy to learn, use and teach.
Request sample